Medically Reviewed by Lucas Rosa, PhD in Molecular Biology
Discover the vital roles of cortisol and learn how to maintain a healthy balance of it.
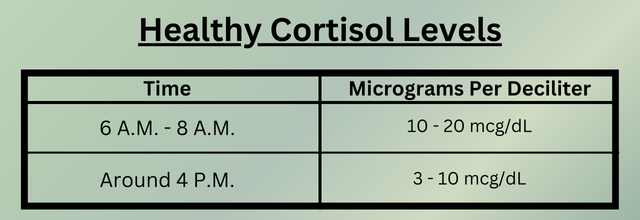
What Is Cortisol?
Cortisol is produced by the adrenal glands above our kidneys and is released in response to stress as part of our body’s natural “fight-or-flight” mechanism.
This mechanism helps our bodies handle immediate threats by preparing them for action. It increases heart rate, boosts energy, and heightens alertness, giving us the competitive edge we need when dealing with stress.
While cortisol is vital for our bodies to respond to short-term stress, it also plays vital roles in other various functions within our bodies like blood sugar levels, immunity, and brain regulation.
The Vital Roles of Cortisol
- Blood Sugar Levels: Cortisol helps maintain blood sugar levels by influencing glucose production and fat storage. It helps ensure your body has enough energy to respond to stress.
- Blood Pressure: Elevated cortisol levels can cause high blood pressure, and similarly, low cortisol levels can cause low blood pressure.
- Immune Function: Cortisol is crucial in regulating the immune system, helping to control inflammation, and preventing our body from overreacting to minor infections or injuries.
- Stress Response: When we’re under stress, cortisol is released to prepare our body for a quick reaction. It increases blood flow to muscles, speeds up breathing, and improves focus, all of which help us respond to immediate stressors.
- Brain and Mood Regulation: Cortisol helps stimulate the production and release of brain neurotransmitters that regulate mood and cognition. In this way, it plays a vital role in maintaining mental clarity and emotional stability.
- Sleep-Wake Cycle: Cortisol plays a key role in wakefulness; its levels are lower when we are about to sleep and peak when we are about to wake up.

The Effects of High Cortisol Levels
Although cortisol is crucial for overall function, persistently elevated levels due to chronic stress can negatively impact both physical and mental well-being. Here’s what happens when cortisol stays elevated for too long:
- Physical Symptoms: Prolonged high cortisol levels can disrupt digestion and contribute to abdominal weight gain, potentially causing severe conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Emotional and Mental Symptoms: Excess cortisol in the body can interfere with sleep, making it difficult to fall or stay asleep while also triggering irritability, anxiety, and mood swings.
- Long-term Health Risks: Long-term effects of elevated cortisol can weaken the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections while also raising the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes.

The Effects of Low Cortisol Levels
While high cortisol is dangerous, conversely, insufficient cortisol can also significantly affect our health. Low cortisol levels in the body can lead to symptoms such as:
- Fatigue and Low Energy: Low cortisol can leave you feeling chronically tired and drained, even after a full night’s sleep.
- Dizziness and Muscle Weakness: A lack of cortisol can result in dizziness, fainting, and muscle weakness, as cortisol plays a key role in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
- Conditions Like Addison’s Disease: Addison’s disease is a condition that occurs when the adrenal glands are damaged and fail to produce enough cortisol. Symptoms include severe fatigue, weight loss, and low blood sugar levels.
- Weakened Immunity: Similar to high cortisol levels, low cortisol levels can also weaken your immune system, increasing vulnerability to infections and other health complications.

Achieving a Healthy Cortisol Balance
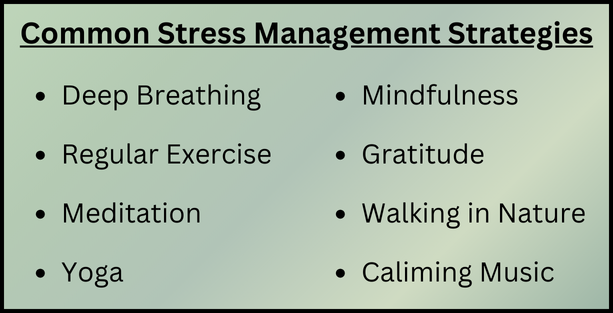
Maintaining a healthy balance of cortisol is essential for overall health and well-being. Thankfully, there are various natural methods to help regulate cortisol levels:
- Stress Management: Reducing stress is the most effective way to maintain healthy cortisol levels. Activities like yoga, mindfulness, Tai Chi, meditation, and deep breathing exercises stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, encouraging relaxation and balanced cortisol levels.
- Regular Exercise: Incorporating regular physical activity, particularly moderate exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling, supports cortisol regulation and promotes overall well-being. It’s also important to avoid excessive exercise, overtraining can increase cortisol production.
- Sleep and Circadian Rhythm: Adequate, restful sleep of no less than 8 hours is vital for managing cortisol levels. Sleep deprivation can cause cortisol levels to rise, while maintaining a consistent sleep schedule that aligns with your body’s natural circadian rhythm helps keep cortisol levels in check.
- Nutritional Diet: A nutritional diet can also support cortisol balance. Eating foods rich in magnesium (like spinach, almonds, and avocados), vitamin C (such as citrus fruits and bell peppers), and healthy fats (like chia seeds and fatty fish) can help manage cortisol levels.
- Limit Stimulants: Over-consuming caffeine and sugar can spike cortisol levels, so it’s important to limit intake of these substances to keep balanced cortisol levels. Instead, focus on balanced meals that keep your blood sugar stable throughout the day.
Tips for Managing Cortisol Levels
Here are some simple lifestyle changes you can incorporate to help manage cortisol and keep it at a healthy level:
- Create a Daily Routine: Consistency is key when it comes to managing stress. Create a balanced daily routine that incorporates time for relaxation, work, exercise, and sufficient sleep. This helps keep cortisol levels steady throughout the day.
- Prioritize Relaxation: Make time for relaxation techniques that help calm your nervous system, such as taking walks in nature or engaging in hobbies you enjoy.
- Avoid Overworking: A healthy work-life balance is essential for managing stress. Avoid long hours or burnout by taking regular breaks and purposely spending quality time with loved ones or in leisure activities.
- Connect with Others: Building a strong social support network can help reduce stress and lower cortisol levels. Healthy, positive relationships act as a buffer against stress, enhancing overall well-being.

Conclusion
Cortisol is an essential hormone for stress management, and maintaining a healthy balance is crucial for both physical and mental health. Chronically high cortisol levels can lead to a host of issues, including weight gain and anxiety, while too little cortisol can leave us feeling fatigued and weak.
Maintaining cortisol balance is an ongoing process that requires lifestyle adjustments, but the results are well worth it. By implementing stress-reducing practices, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and eating a balanced diet, you can help maintain optimal cortisol levels. Making these adjustments not only helps lower stress but also cultivates a healthier and more harmonious way of living.
Sources:
Çay, Mahmut. “The Effect of Cortisol Level Increasing due to Stress in Healthy Young Individuals on Dynamic and Static Balance Scores.” Northern Clinics of Istanbul, vol. 5, no. 4, 29 May 2018, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6371989/, https://doi.org/10.14744/nci.2017.42103.
Cleveland Clinic. “Cortisol: What It Is, Function, Symptoms & Levels.” Cleveland Clinic, 12 Oct. 2021, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/22187-cortisol.
Healthdirect. “The Role of Cortisol in the Body.” Healthdirect, Healthdirect Australia, 11 Feb. 2019, www.healthdirect.gov.au/the-role-of-cortisol-in-the-body.
John Hopkins Medicine. “Adrenal Insufficiency (Addison’s Disease).” John Hopkins Medicine, 2023, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/underactive-adrenal-glands–addisons-disease.
WebMD. “What Is Cortisol?” WebMD, WebMD, 6 Feb. 2017, www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/what-is-cortisol.
The American Institute of Stress. “18 Quick Ways to Relax Instantly, according to Science – the American Institute of Stress.” The American Institute of Stress, 11 Feb. 2022, www.stress.org/news/18-quick-ways-to-relax-instantly-according-to-science/.
Check Out
HF Swaps
Better products for better hormone health.









